 Plug Valve. This valve controls the flow of fluid through a conical or cylindrical plug which has a hole through it, and permits the fluid passage when this hole is aligned with the pipe axis.
Plug Valve. This valve controls the flow of fluid through a conical or cylindrical plug which has a hole through it, and permits the fluid passage when this hole is aligned with the pipe axis.
Like ball valves, plug valves are quick and easy to use, requiring only a 90° turn around the handle to open or close the valve.
When these valves are closed, they contain the fluid in the ball or plug, which can create problems when used with corrosive fluids.
See figure

Types of Plug valves
The plug valves are manufactured in a lubricated or non-lubricated design and with different types of openings.
Plug valves are available with conical and cylindrical shaped plugs. The cylindrical plug provides larger orifice openings equal to or greater than the flow area of the pipe.
Lubricated Plug valves
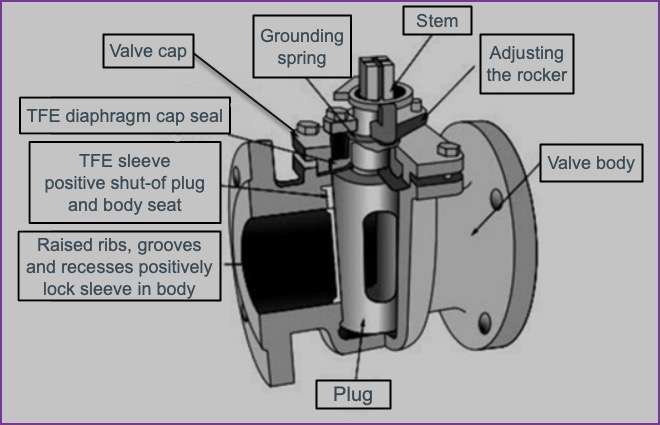
The plug of a lubricated plug valve is provided with a cavity in the middle along its axis. This cavity is closed at the bottom and fitted with a sealing device at the top. The sealant is injected into the cavity, and a check valve located below the injection fitting prevents the sealant from flowing back. The sealant oozes from the central cavity through the radial holes in the lubricant grooves which extend along the seat surface of the plug. The sealing agent or lubricant fulfills the following functions:
- Establishes a renewable seal between the plug and the body. Internal leaks are therefore avoided or minimized.
- Protects the seating areas from corrosion.
- Acts as a lube, reducing the force needed to open or close the valve. The lubricant pressure developed by a turn of the lubricant screw or injection of lubricant with a pressure gun exerts a powerful hydraulic jacking action on the plug, momentarily raising the seat and facilitating the turn. Since the lubricant pressure is greater than the pipe pressure, it is practically impossible for solids to lodge between the valve body and the plug.
The type of sealant to be used must be compatible with the flow medium in the pipe. The sealant should not dissolve or be washed by the fluid. The washed or dissolved sealant could contaminate the fluid, and the seal between the plug and the body would be destroyed, resulting in leaks. Additionally, the sealant used must be capable of supporting the temperature of the fluid.
Lubricated plug valves are generally manufactured in dimensions ranging from NPS¹ to 36 (DN 15 to 900). They can be used for applications with pressures higher than 2500 psi (17250 kPa). They have been used in air, gases, acids, alkalis, water, stem, oils, fuels, and more. Lubricated plug valves are less subject to seizing or wear and may exhibit somewhat greater resistance to corrosion in some service environments.

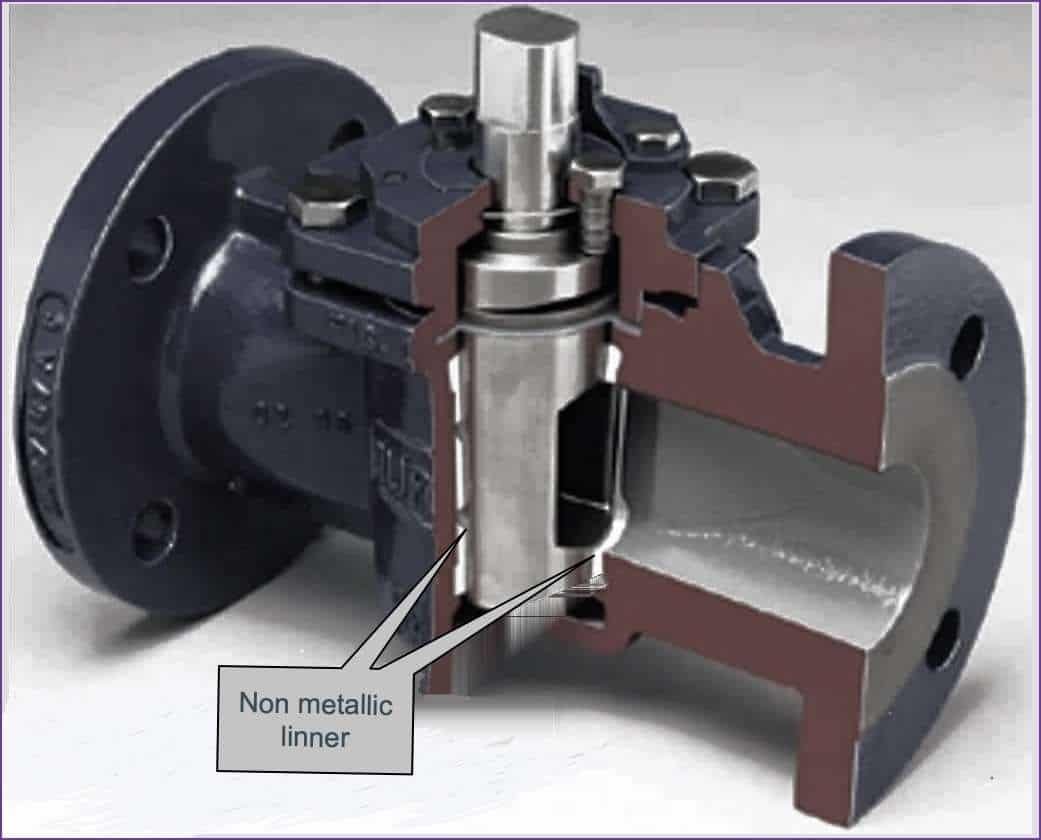
Non lubricated plug valve
Non-Lubricated styles don’t use grease for sealing. This design usually covers or vulcanizes an elastomer on the plug or body (Buna, Viton, EPDM, Teflon or other) to reach near zero leakage in closed position. The tapered and polished plug acts like a wedge and presses the sleeve against the body.
In this way, the non-metallic cover reduces the friction between the plug and the body.
Unlubricated valves are limited by the temperature and chemical compatibility of the non-metallic material.
Un-lubricated valves are normally used for low-pressure piping, and their seats tend to deteriorate more rapidly due to dust, wear, dirt and other debris compared to lubricated valves.
Non-Lubricated plug valves are used often in applications of water & wastewater.

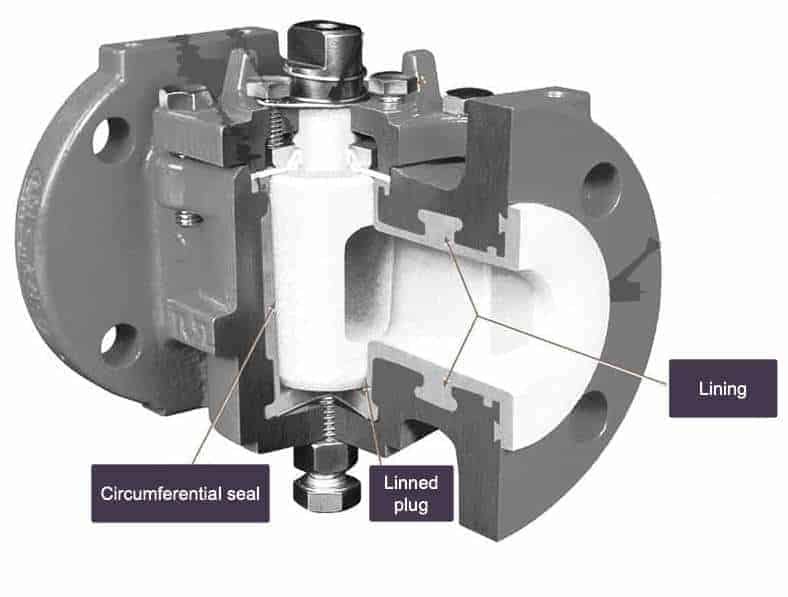
Lined Plug Valve
Lined valves are equipped with an encapsulated plug rotating in a fully lined body that provides a long-lasting valve.
All surfaces in wet valve parts are covered, for example, with PFA to protect valve life from chemical corrosion. Injection molded with PFA lining is free of pinholes, cracks, swelling, and locally uneven thickness, and prevents service issues like foliation, stress cracking and fluid permeation.
Port in the tapered plug
The port of the tapered plug is generally rectangular. Nevertheless, valves are also available in round ports. The major models or types of valves are identified as regular, Venturi, short, round port and multiport.
The plugs are typically tapered down, while in some cases, they are tapered up.
Plug valves are also available with cylindrical plugs. Cylindrical caps have larger orifice openings equal to or greater than the pipe flow area.
The regular pattern employs the tapered form of port openings, the area of which is from 70 to 100 percent of the internal pipe area. In some cases, the face-to-face lengths are greater than those of standard gate valves. The Venturi model provides a streamlined flow, which reduces the size of the port. The port opening area represents approximately 40 to 50 percent of the inside area of the pipeline. In most of the plug valves, the port opening varies from 60 to 70 percent of the pipe area.
Multi-port plug valves
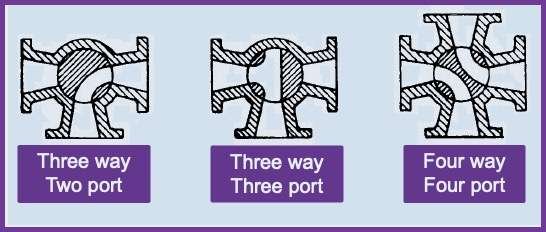
The full bore round port model has a circular port through the plug and body equal to or greater than the internal diameter of the pipe or fitting. The operational performance is equal to or superior to that gate valves of the same size. The use of multi-port valves is advantageous in many plants because it simplifies piping and operational convenience.
Multiport valves are used for transfer lines and bypass services. A single multiport valve can substitute three or four valves or other types of globe valves.
Plug Valve Application
Plug valve is used for on-off services and capable of providing bubble-tight shut-off.
It can be applied to different types of fluid services such as air, gas, vapor, Hydrocarbons, slurries, mud, and sewage applications.
The valve can be used in vacuum applications.
Pros and cons of plug valves.
Advantages.
Fast shutdown operation.
Minimal resistance to flow
Smaller in size compared to most other valves.
Disadvantages.
Requires significant force to operate because of high friction.
NPS 4 and larger valves need an actuator.
Generally, plug valves costs are much larger than ball valves.
See the next post about Examples of Pressure Relief Device
Plug Valve – Calculate Man Hours