 A comprehensive list of construction insurance types and their definitions.
A comprehensive list of construction insurance types and their definitions.
The estimate of financial costs in an economic proposal includes the insurance cost and the financial cost itself.
This post examines the costs and types of insurances and sureties of the bond.
Insurance Requirements for Bid / Types of Construction Insurance
Time needed: 15 minutes
- Determine what types of coverage the client requires
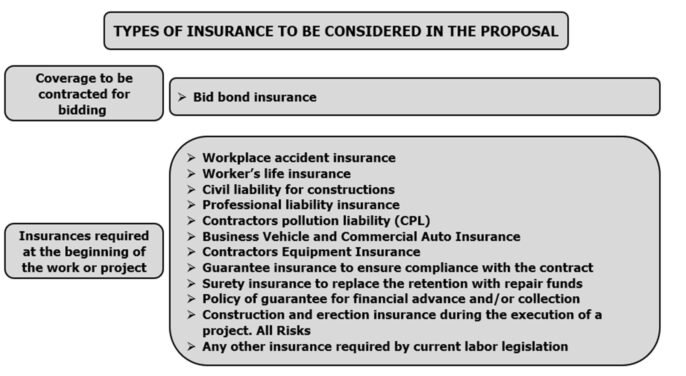
Tender documents should set out the type of insurance required by the customer, coverage and insured amounts.
The type of insurance to be included in the proposal is divided into tender guarantees and guarantees necessary for the performance of the contract.
We must ensure that there is no lack of any other insurance required under current labor laws.
The type of insurance currently used in the construction sector is summarized in the figure below: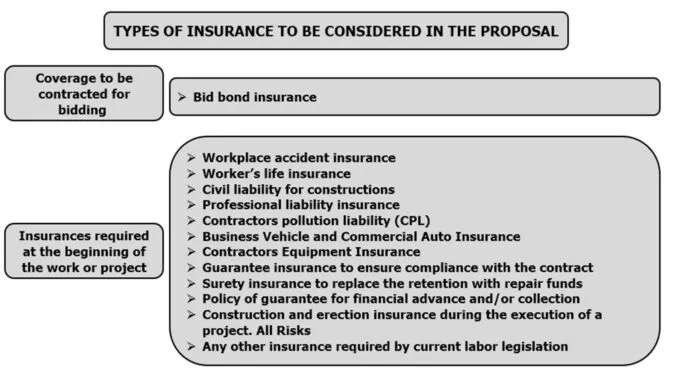 This image ALT text is: The picture shows a summary, prepared by Gustavo Cinca, detailing the types of insurance that are currently used to carry out industrial work.. Types of Construction Insurance – Calculate Man Hours
This image ALT text is: The picture shows a summary, prepared by Gustavo Cinca, detailing the types of insurance that are currently used to carry out industrial work.. Types of Construction Insurance – Calculate Man Hours - Confirm which insurance companies are accepted by the client
In most cases, in the tender documents, the buyer lists the authorized insurers.
If the information is not included in the tender documents, we should submit a written request to the client.
- Request quotation from authorized insurance companies
After defining all of the above, the final step is to ask for quotes from various insurance companies in order to choose the most convenient.
For the Insurance Company’s choice, not only should the price be evaluated, but also the certainty that the coverage includes all the risks to be covered.
To do so, it is convenient to seek the advice of a risk manager and an insurance consultant.
FAQs:
What is a bid bond?
Bid Bond Insurance, also known as a Bid Bond Guarantee, is a type of insurance which guarantees the contractor’s commitment to a construction project. It is generally necessary in the tendering process for both public and private construction projects.
When a contractor submits a bid for a project, they may be required to provide a bid bond as a form of security to the project owner or developer.
The bid bond protects the owner in case the contractor is awarded the project, but fails to enter into a contract or fails to provide the required performance and payment bonds.
If the Contractor fails to meet its obligations following project award, the Project Owner may claim the Bid Bond.
The insurer will then compensate the owner until the amount of the surety. The contractor is usually responsible for reimbursing the insurer for any claims paid.
Bid bond insurance provides financial protection to project owners, ensuring they have recourse if a successful bidder does not act on the contract.
It helps maintain the integrity of the bidding process and provides assurance to project owners that contractors take their bids seriously.
The bidder assigns the cost of these policies to overhead.
Insurance required for contractors: Workplace accident insurance
Definitions of Workplace accident insurance
Workplace accident insurance, also known as workers’ compensation insurance, is a type of insurance coverage that provides financial protection to employees who suffer injuries or illnesses as a result of their work.
It is designed to ensure that employees receive necessary medical treatment and wage replacement benefits, while also protecting employers from lawsuits related to workplace injuries.
Here are some key points about workplace accident insurance:
Coverage: Workplace accident insurance covers employees for injuries or illnesses that occur during the course of their employment. It typically includes accidents, such as slips and falls, as well as occupational diseases or illnesses that develop over time due to work conditions.
Medical Expenses: The insurance policy typically covers medical expenses related to the treatment of work-related injuries or illnesses. This can include hospitalization, doctor’s visits, medications, surgeries, rehabilitation, and other necessary medical treatments.
Wage Replacement: If an employee is unable to work due to a work-related injury or illness, workplace accident insurance provides wage replacement benefits. These benefits usually cover a portion of the employee’s lost wages, typically a percentage of their pre-injury earnings, and are meant to help the employee meet their financial obligations during the recovery period.
Disability Benefits: In cases where the work-related injury or illness results in a permanent disability or impairment, workplace accident insurance may provide additional disability benefits to compensate for the loss of earning capacity.
Legal Protection: By providing workers’ compensation coverage, employers are generally protected from being sued by employees for workplace injuries or illnesses. Workers’ compensation is considered a no-fault system, meaning that employees are entitled to benefits regardless of who was at fault for the accident.
Mandatory Requirement: Workplace accident insurance is often a legal requirement for employers in many jurisdictions. Employers are typically required to carry workers’ compensation insurance to provide coverage for their employees in case of work-related injuries or illnesses.
Insurance required for contractors: Life insurance for workers
Life insurance for workers, also known as group life insurance or employer-sponsored life insurance, is a type of life insurance coverage provided by employers to their employees. It is a benefit offered as part of an employee benefits package, and its purpose is to provide financial protection to employees and their families in the event of the employee’s death.
Here are some key points about life insurance for workers:
Coverage: Life insurance for workers provides a death benefit to the designated beneficiaries if the insured employee passes away during the coverage period. The death benefit is typically a lump sum payment and is intended to provide financial support to the employee’s family, such as covering funeral expenses, paying off debts, replacing lost income, or funding education expenses.
Group Coverage: This type of life insurance is provided to a group of employees rather than individual policies for each employee. The employer negotiates a group life insurance policy with an insurance provider, and all eligible employees are automatically covered under the policy.
Employer-Paid or Employee-Paid: The cost of the life insurance coverage can be either fully paid by the employer as an employee benefit or shared between the employer and the employee through payroll deductions.
Simplified Underwriting: Group life insurance typically involves simplified underwriting compared to individual life insurance policies.
This means that employees may not be required to undergo a medical examination or provide detailed health information to qualify for coverage. However, there may still be certain eligibility criteria, such as minimum hours worked or a waiting period, before an employee becomes eligible for coverage.
Portability and Conversion: Depending on the terms of the policy, employees may have the option to continue their life insurance coverage if they leave the company.
This is often referred to as portability. Additionally, some policies may allow employees to convert their group coverage into individual policies upon leaving employment.
Benefit Amount: The amount of coverage provided under group life insurance is usually a multiple of the employee’s salary, such as one or two times the annual salary. However, employers may offer different coverage options or allow employees to purchase additional coverage through voluntary contributions.
Tax Considerations: In many countries, the premiums paid by employers for group life insurance are often tax-deductible expenses. Additionally, the death benefit received by beneficiaries is generally tax-free.
Insurance required for contractors: Civil responsibility for construction
Civil responsibility in the context of construction refers to the legal obligation of construction professionals or entities to compensate for any damage, injury, or loss caused to third parties as a result of their construction activities.
Construction projects involve various parties, including contractors, architects, engineers, and subcontractors, and each of them may have civil responsibilities depending on their roles and contractual agreements.
Duty of Care: Construction professionals have a duty of care to ensure that their actions do not cause harm to others. They are expected to follow accepted industry standards, exercise reasonable skill and care, and comply with relevant building codes, regulations, and safety guidelines.
Negligence: If a construction professional fails to meet the expected standard of care, resulting in damage or injury, they may be held liable for negligence. Negligence occurs when there is a breach of the duty of care, causing foreseeable harm to others.
Types of Damages: Civil responsibility in construction can involve a wide range of damages, including property damage, personal injury, economic loss, and loss of use. For example, if a construction defect leads to a building collapse causing injuries to occupants, the responsible party may be required to compensate for medical expenses, property damage, lost income, and pain and suffering.
Contractual Obligations: Civil responsibility in construction is often governed by contractual agreements. Contracts may specify the standards of performance, responsibilities, and liabilities of each party involved in the construction project.
Parties can be held accountable for breaching their contractual obligations and may be required to compensate for resulting damages.
Professional Liability Insurance: Construction professionals, such as architects and engineers, typically carry professional liability insurance, also known as errors and omissions (E&O) insurance.
This insurance provides coverage for damages resulting from professional negligence or errors in design, specifications, or construction supervision.
Statutory Requirements: Construction projects are subject to regulatory requirements and building codes set by local, regional, or national authorities.
Failure to comply with these requirements can result in civil liability, as well as legal penalties or fines.
Dispute Resolution: In the event of a construction-related dispute, the parties may resort to alternative dispute resolution mechanisms, such as mediation or arbitration, to resolve their differences without going to court. These mechanisms can help parties reach a settlement and avoid protracted litigation.
Insurance required for contractors: Professional liability insurance
It may be applied to various sectors
Professional liability insurance, also known as errors and omissions (E&O) insurance, protects professionals from financial losses resulting from claims of negligence or inadequate work.
It is designed to provide coverage for professionals who provide advice, services, or expertise to clients.
Here are some key points about professional liability insurance:
Coverage: Professional liability insurance covers professionals against claims made by clients or third parties alleging errors, omissions, negligence, professional misconduct, or failure to deliver promised services. It typically includes legal defense costs, settlements, and judgments associated with such claims.
Professions Covered: Various professions can benefit from professional liability insurance, including but not limited to accountants, consultants, architects, engineers, real estate agents, etc..
Types of Claims: Claims covered by professional liability insurance can include malpractice, negligence, misrepresentation, violation of good faith and fair dealing, and failure to meet professional standards.
Importance: Professional liability insurance is important because even professionals who excel at their work can make mistakes or face baseless claims. A single claim can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal expenses, which can be financially devastating without adequate insurance protection.
Tailored Coverage: Professional liability insurance policies can be tailored to the specific needs of different professions and industries. The coverage limits, deductibles, and policy terms can vary depending on factors such as the nature of the work, the size of the business, and the level of risk involved.
Legal Requirements: In some professions, professional liability insurance is a legal or regulatory requirement.
Claims Process: In the event of a claim, the insured professional must notify the insurance company promptly. The insurance company will typically investigate the claim, provide legal defense if necessary, and negotiate settlements or represent the insured in court, depending on the circumstances.
Exclusions: Like any insurance policy, professional liability insurance has certain exclusions. Common exclusions may include intentional wrongdoing, criminal acts, bodily injury or property damage claims (covered by general liability insurance), and claims related to other types of insurance such as workers’ compensation.
Insurance required for contractors: Contractors pollution liability (CPL)
Definitions of Contractors pollution liability (CPL) insurance.
Contractors pollution liability (CPL) insurance is a type of insurance coverage specifically designed to protect contractors and subcontractors against liabilities arising from pollution-related risks and incidents. It provides coverage for damages, cleanup costs, and legal expenses associated with pollution incidents that occur during construction or contracting activities.
Here are some key points about Contractors’ Pollution Liability (CPL) insurance:
Coverage: CPL insurance offers protection for contractors in the event of pollution-related incidents, such as accidental releases of pollutants, environmental damage, or contamination caused by their work activities. It covers both sudden and gradual pollution events.
Scope of Coverage: CPL insurance typically covers various types of pollution, including pollution caused by hazardous materials, mold, asbestos, lead, and other contaminants.
It may also provide coverage for third-party bodily injury, property damage, and cleanup costs resulting from pollution incidents.
Covered Parties: CPL insurance is typically purchased by contractors and subcontractors involved in construction, renovation, or remediation projects. It may be applicable to various sectors, including general contractors, environmental remediation contractors, construction managers, and specialty trade contractors.
Policy Features: CPL insurance policies can be customized to meet the specific needs of contractors. Coverage limits, deductibles, and policy terms can vary depending on factors such as the size of the contractor’s operations, the types of projects undertaken, and the level of risk involved.
Exclusions: CPL insurance policies may have certain exclusions, such as intentional pollution, known pollution conditions, and certain types of professional services.
It’s crucial for contractors to review their policy carefully and understand the specific exclusions and limitations.
Contractual Requirements: In some cases, contractors may be required to carry CPL insurance as a contractual obligation.
Clients or project owners may include it as a prerequisite for awarding a contract, particularly for projects involving environmental risks or sensitive locations.
Claims Process: In the event of a pollution incident, the contractor must notify the insurance company promptly.
The insurance company will investigate the claim, provide legal defense if necessary, and cover costs associated with the incident, including cleanup, remediation, and potential liabilities.
Risk Management: Contractors should also implement effective risk management practices to minimize the likelihood of pollution incidents and associated liabilities. This may include proper handling, storage, and disposal of hazardous materials, adherence to environmental regulations, and proactive safety measures.
Insurance required for contractors: Business and commercial motor vehicle insurance
Business and commercial motor vehicle insurance provides coverage for vehicles used for business purposes.
Whether you have a single vehicle or a fleet of vehicles, this type of insurance is designed to protect your business against financial losses resulting from accidents, theft, or other damages involving your vehicles. Here are some key points to understand about business and commercial motor vehicle insurance:
Coverage: Commercial motor vehicle insurance typically provides coverage for liability, physical damage, and other specific risks associated with business-related vehicle use.
Liability coverage: This protects your business if you or your employees cause injury or property damage to others while operating the vehicles for business purposes. It covers legal expenses, medical costs, and property repairs or replacement.
Physical damage coverage: This includes comprehensive and collision coverage. Comprehensive coverage protects against non-collision incidents such as theft, vandalism, fire, or natural disasters.
Collision coverage provides protection for damages resulting from collisions with other vehicles or objects.
Uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage: This covers you and your employees if you’re involved in an accident with a driver who is at fault but has insufficient or no insurance.
Medical payments coverage: This covers medical expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of who is at fault for the accident.
Cargo coverage: If your business involves transporting goods, you may need cargo coverage to protect the value of the goods in case of damage or theft.
Non-owned vehicle coverage: If your employees occasionally use their personal vehicles for business purposes, this coverage can protect your business if they’re involved in an accident while doing so.
Vehicle Types: Business and commercial motor vehicle insurance can cover a wide range of vehicles, including cars, trucks, vans, delivery vehicles, buses, taxis, and specialized vehicles like construction and assembly machinery.
The insurance can be tailored to suit your specific needs based on the types of vehicles your business uses.
Premiums: The cost of commercial motor vehicle insurance premiums depends on various factors such as the number and type of vehicles, their usage, the driving records of the employees, the location of your business, and the coverage limits you choose. Insurance companies may also consider the industry in which your business operates, as certain industries may have higher risk profiles.
Legal Requirements: Business and commercial motor vehicle insurance is often legally required, especially for commercial vehicles.
The specific requirements can vary by jurisdiction, so it’s essential to understand and comply with the regulations in your area.
Risk Management: Maintaining a good safety record, implementing driver training programs, and properly maintaining your vehicles can help reduce the risks associated with commercial vehicle operations. Insurance companies may offer discounts or incentives for businesses that demonstrate effective risk management practices.
Insurance required for contractors: Contractors Equipment Insurance
Definitions of Contractors Equipment Insurance
Contractors Equipment Insurance is a type of coverage specifically designed to protect contractors and construction companies against financial losses arising from damage, theft, or loss of their equipment and tools.
Contractors often rely on various types of equipment and machinery to carry out their work, and these assets can be costly to repair or replace if they are damaged or stolen.
Contractors Equipment Insurance typically provides coverage for:
Owned equipment: This includes coverage for the contractor’s own equipment, such as excavators, bulldozers, cranes, generators, power tools, and other machinery.
Rented or leased equipment: If contractors rent or lease equipment for their projects, this coverage can protect them from losses associated with damage or theft of the rented or leased items.
Equipment in transit: Coverage can extend to equipment and tools while they are being transported to and from job sites.
Equipment breakdown: This coverage can help cover the costs of repairing or replacing equipment in the event of mechanical or electrical breakdowns.
Loss of income: In case a covered loss leads to a business interruption, this coverage can reimburse the contractor for lost income during the downtime.
Accessories and attachments: Coverage can be extended to include accessories and attachments that are essential to the operation of the insured equipment.
It’s important to note that Contractors Equipment Insurance typically does not cover liabilities resulting from accidents or injuries caused by the equipment. For such liabilities, contractors usually need General Liability Insurance or Workers’ Compensation Insurance.
Insurance required for contractors: Guarantee insurance to ensure compliance with the contract
Guarantee insurance, also known as contract guarantee insurance or performance bond insurance, is a type of insurance designed to ensure compliance with the terms and conditions of a contract.
It provides financial protection to the beneficiary of the contract (usually the project owner or client) in the event that the contractor fails to fulfill their contractual obligations.
When a contractor enters into a contract, the project owner may require them to provide a guarantee or bond as a form of security.
This guarantee serves as a promise that the contractor will complete the project as specified in the contract, and it provides reassurance to the project owner that they will be compensated if the contractor fails to meet their obligations.
Here’s how guarantee insurance works:
Contractor obtains the insurance: The contractor purchases guarantee insurance from an insurance company or a surety bond provider.
The insurance provider evaluates the contractor’s financial stability, track record, and ability to fulfill the contract before issuing the guarantee.
Terms of the guarantee: The guarantee insurance policy outlines the terms and conditions under which the insurance provider will compensate the project owner if the contractor defaults on the contract.
These terms typically include the amount of coverage, the scope of the guarantee, and the triggering events that would lead to a claim.
Contractor defaults on the contract: If the contractor fails to fulfill their contractual obligations, such as non-completion of the project, substandard work, or financial default, the project owner can make a claim on the guarantee insurance policy.
Insurance provider compensates the project owner: If the claim is valid and falls within the terms of the policy, the insurance provider will compensate the project owner up to the coverage amount specified in the policy.
The insurance provider may then seek reimbursement from the contractor for the amount paid out.
Guarantee insurance provides protection to the project owner against financial losses resulting from the contractor’s failure to meet their obligations.
It helps ensure that the project owner can complete the project or hire another contractor without incurring significant additional costs.
It’s important to note that guarantee insurance is different from liability insurance. Liability insurance protects against claims for injury or property damage caused by the contractor’s actions, whereas guarantee insurance focuses on the contractor’s performance and compliance with the contract terms.
Insurance required for contractors: Surety insurance to replace the retention with repair funds
Surety insurance is a type of insurance that provides financial protection to the project owner or client in the event that the contractor fails to fulfill their contractual obligations.
It is commonly used in construction projects to replace the traditional practice of withholding retention funds with repair funds.
In many construction contracts, a certain percentage of the contract price is withheld by the project owner as retention funds.
These funds are typically intended to provide a form of security for the project owner in case the contractor does not complete the project satisfactorily or fails to address any defects or issues that may arise during the warranty period.
Surety insurance offers an alternative approach to retention funds by providing a guarantee from a third-party surety company.
Here’s how it works:
Contractor obtains surety insurance: The contractor purchases surety insurance from a surety company. The surety company evaluates the contractor’s financial stability, track record, and ability to fulfill the contract before issuing the insurance.
Terms of the surety insurance: The surety insurance policy outlines the terms and conditions under which the surety company will provide financial compensation to the project owner if the contractor fails to meet their contractual obligations. This includes addressing defects or issues that may arise during the warranty period.
Replacement of retention funds: Instead of withholding retention funds from the contractor, the project owner relies on the surety insurance as a form of financial security.
The surety insurance replaces the need for retention funds by providing assurance to the project owner that they will be compensated if the contractor fails to fulfill their obligations.
Contractor defaults on the contract: If the contractor fails to meet their obligations, such as non-completion of the project or failure to address defects, the project owner can make a claim on the surety insurance policy.
Surety company compensates the project owner: If the claim is valid and falls within the terms of the policy, the surety company will compensate the project owner up to the coverage amount specified in the policy.
The surety company may then seek reimbursement from the contractor for the amount paid out.
By utilizing surety insurance instead of retention funds, the project owner can potentially free up cash flow that would otherwise be tied up in withheld funds.
It also provides an additional layer of financial protection and assurance in case the contractor fails to fulfill their obligations.
It’s important to note that surety insurance does not replace other types of insurance coverage, such as liability insurance or professional indemnity insurance, which may still be required to address other types of risks associated with the project.
Insurance required for contractors: Policy of guarantee for financial advance and/or collection
A policy of guarantee for financial advance and/or collection is a type of insurance coverage that provides protection to businesses or individuals who have advanced funds or made payments to another party.
This insurance policy safeguards the insured party against the risk of non-repayment or non-collection of the advanced funds.
Here’s how a policy of guarantee for financial advance and/or collection typically works:
The insured party requests a guarantee: The party who has advanced funds or made payments (referred to as the beneficiary) seeks a guarantee from an insurance provider to protect their financial interest.
Evaluation and underwriting: The insurance provider evaluates the request and assesses the risk associated with the guarantee. This involves examining the financial standing and creditworthiness of the party to whom the funds have been advanced (referred to as the debtor).
Issuance of the guarantee policy: If the insurance provider determines that the risk is acceptable, they issue a guarantee policy to the beneficiary. The policy outlines the terms and conditions under which the insurance provider will provide compensation to the beneficiary.
Default or non-repayment: In the event that the debtor defaults on the repayment or fails to fulfill their obligations, the beneficiary can make a claim under the guarantee policy.
Compensation by the insurance provider: If the claim is valid and falls within the terms of the policy, the insurance provider compensates the beneficiary for the amount of the financial advance or payment that was not repaid or collected.
The insurance provider may then seek recovery from the debtor for the amount paid out.
A policy of guarantee for financial advance and/or collection helps protect businesses or individuals from potential financial losses resulting from non-repayment or non-collection.
It provides an added layer of security when dealing with transactions involving significant sums of money or when dealing with parties whose creditworthiness may be uncertain.
Insurance required for contractors: Any other insurance required by current labor legislation
What are the additional clauses required by the Client?
Generally, the Client requests that insurance policies include the following clauses:
Clause waiving subrogation by the insurer against the Client.
(Known as the non-repetition clause)
Clauses that prevent the insurer from modifying and/or canceling the insurances without prior notice to the Client.
We should note that the Client regularly monitors the validity of each of the policies required in the contract document.
The following post discusses the financial cost in construction projects.
Types of Construction Insurance – Calculate Man Hours.