 Calculating Working Hours: Understanding Variations Across the Globe. This guide explores the concept of working hours and how they differ around the world.
Calculating Working Hours: Understanding Variations Across the Globe. This guide explores the concept of working hours and how they differ around the world.
Defining Work Hours
- Work Hours vs. Unpaid Work: Working hours refer to the time spent on paid work activities. Unpaid activities like household chores or childcare are not included.
- Regulations and Work Week: Many countries regulate working hours through legislation. This includes minimum rest periods, annual holidays, and maximum weekly working hours.
Factors Affecting Working Hours
Individual working hours can vary based on:
Livelihood: The nature of an individual’s job can impact their work schedule.
Economic Conditions: Economic situations can influence work hours.
Location: Geographical location can influence work culture and typical working hours.
Culture: Cultural norms may influence work expectations.
Lifestyle: Personal lifestyle preferences can affect desired work hours.
Standard Work Hours and Overtime
- Normal Working Hours: Legislation often sets limits for working hours per day, week, month, or year.
- Overtime Pay: Employers typically pay higher rates for overtime hours mandated by law.
Standard Workweeks and Overtime Rates
- Global Variations: Standard workweeks range from 35 hours (France) to potentially exceeding 100 hours (North Korean labor camps).
- Overtime Rates: Overtime pay generally ranges from 25% to 50% higher than regular hourly rates.
How Many Hours of Work in a Year?
Let’s break down the annual work hours, considering standard and leap years.
Standard Year:
- Weeks in a year: 365 days ÷ 7 days/week ≈ 52.14 weeks
- Workdays in a year: 52.14 weeks × 5 weekdays/week ≈ 260.71 days
- Work hours in a year: 260.71 days × 8 hours/day ≈ 2085.71 hours
Leap Year:
- Weeks in a year: 366 days ÷ 7 days/week ≈ 52.29 weeks
- Workdays in a year: 52.29 weeks × 5 weekdays/week ≈ 261.43 days
- Work hours in a year: 261.43 days × 8 hours/day ≈ 2091.43 hours
So, in a standard year, you work approximately 2086 hours, and in a leap year, it’s around 2091 hours.
Please note that these are estimates based on a standard 40-hour workweek. Actual work hours can vary depending on factors like overtime, part-time work, and industry-specific schedules.
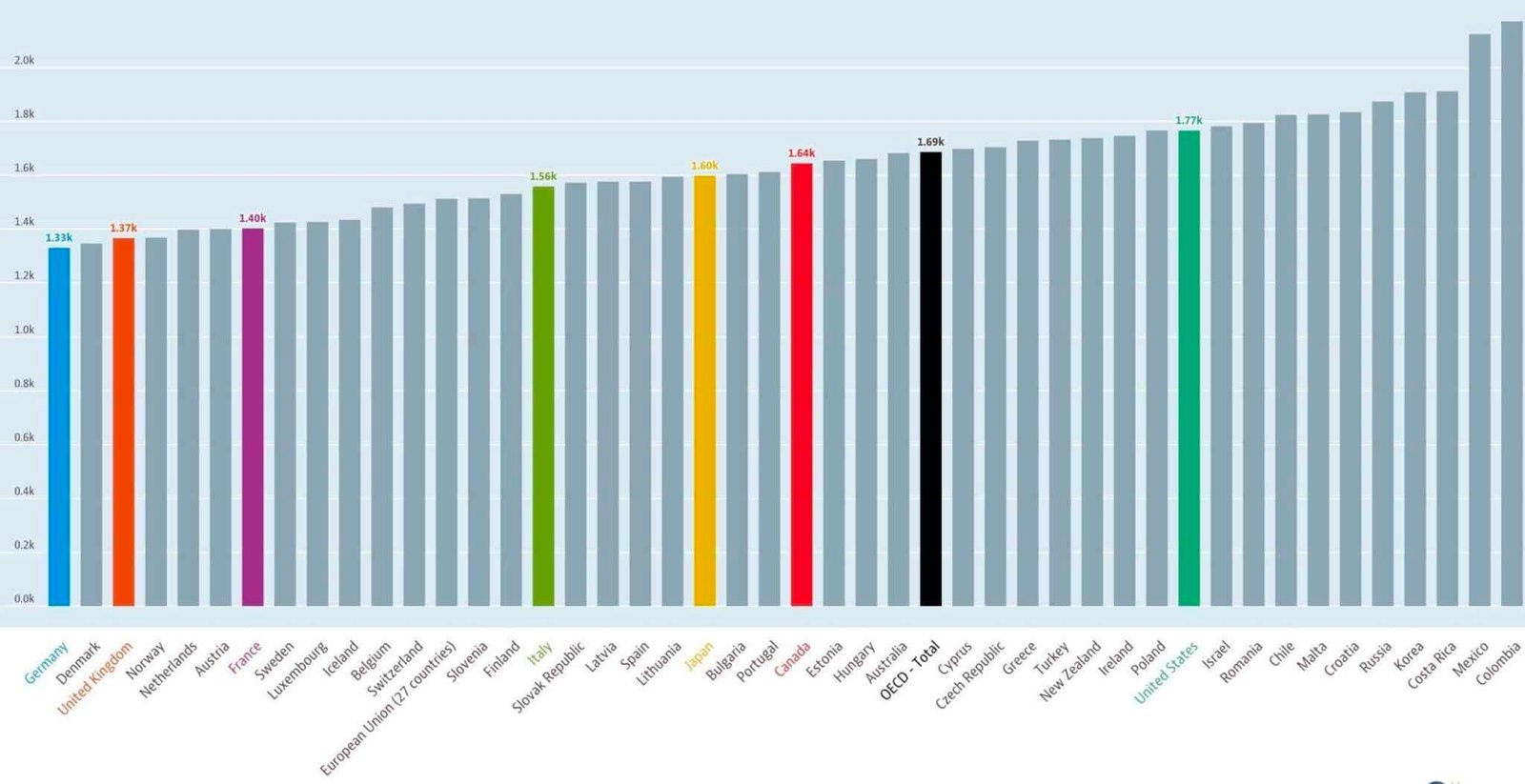
Average Annual Working Hours
This section defines average annual working hours and includes a chart for reference.
The average yearly number of hours worked is defined as the total number of hours actually worked per year divided by the average number of persons in employment per year.
The following chart shows the average annual hours worked by country.
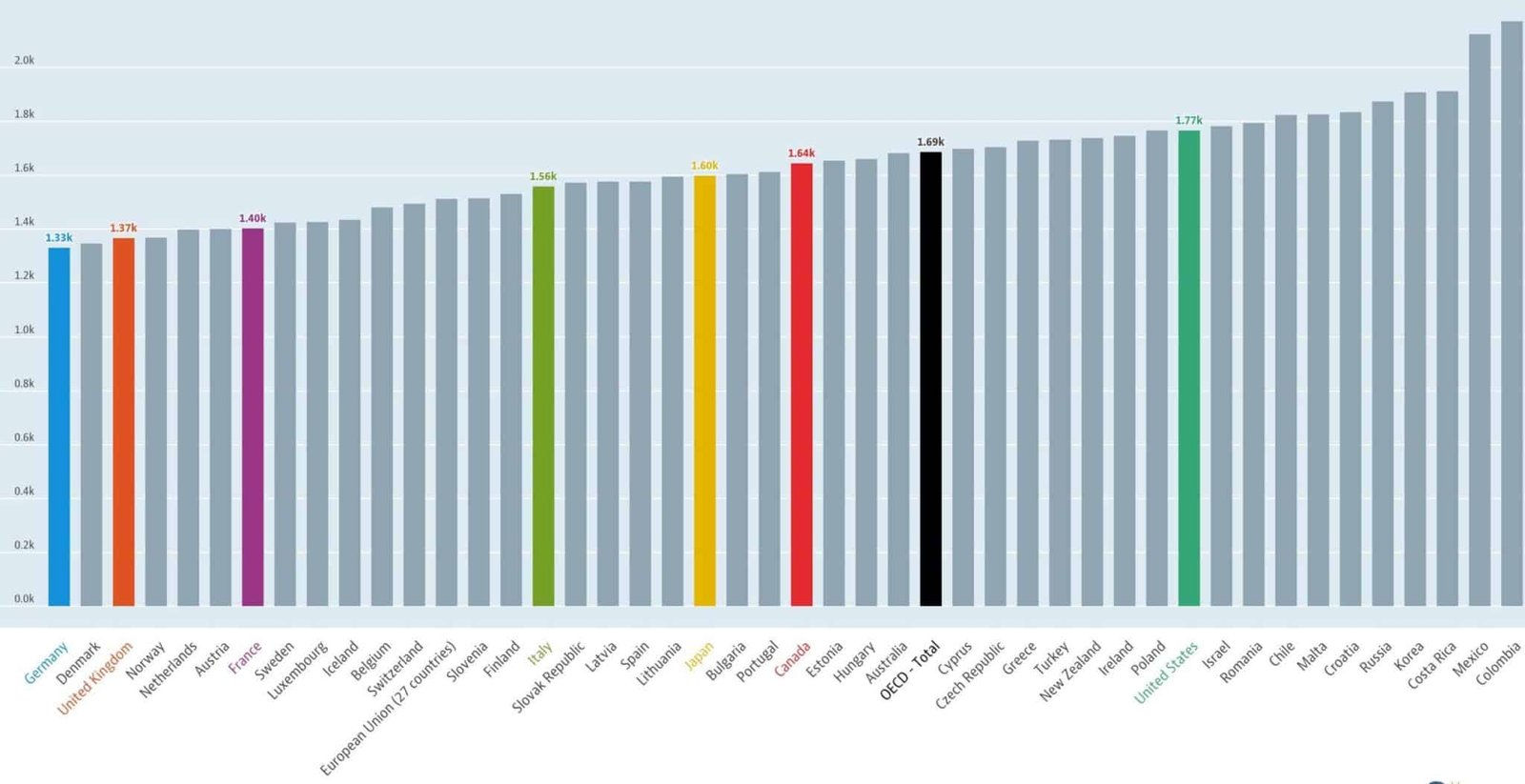
The data are published with the following caution:
The data are intended for comparisons of trends over time they are unsuitable for comparisons of the level of average annual hours of work for a given year due to different sources and calculation methods.
Important Considerations When Interpreting Data
The provided data are best suited for observing trends over time, not direct year-to-year comparisons due to variations in data collection methods.
Real Hours Worked: A Closer Look
This section defines real hours worked, and the factors included and excluded in their calculation.
What’s Included:
- Normal working hours (full-time and part-time)
- Paid and unpaid overtime
- Hours worked in additional jobs
What’s Excluded:
- Time off for statutory holidays
- Paid vacation leave
- Time off due to illness, injury, disability
- Leave for maternity, parental leave, education, or training
- Time off due to slack work, strikes, weather, or other reasons
Who’s Included:
The data covers both employees and self-employed workers. It’s measured by the average number of hours worked per worker per year.
In the next post, we will review some very useful information about the types of valves used in piping.
Calculating Working Hours: Understanding Variations Across the Globe – Calculate Man hours.